JARDIANCE is indicated for:
Type 2 diabetes
exercise, improves glycemic
control in adults with T2D.
Type 2 diabetes and
eCVD
Heart failure
Chronic kidney disease
JARDIANCE is not recommended: to improve glycemic control in patients with T1D, it may increase their risk of diabetic ketoacidosis; to improve glycemic control in patients with T2D with an eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2, it is likely to be ineffective based upon its mechanism of action; for treatment of CKD in patients with polycystic kidney disease or patients requiring or with a recent history of IV immunosuppressive therapy or >45 mg of prednisone or equivalent for kidney disease, it is not expected to be effective in these populations.
JARDIANCE is indicated:
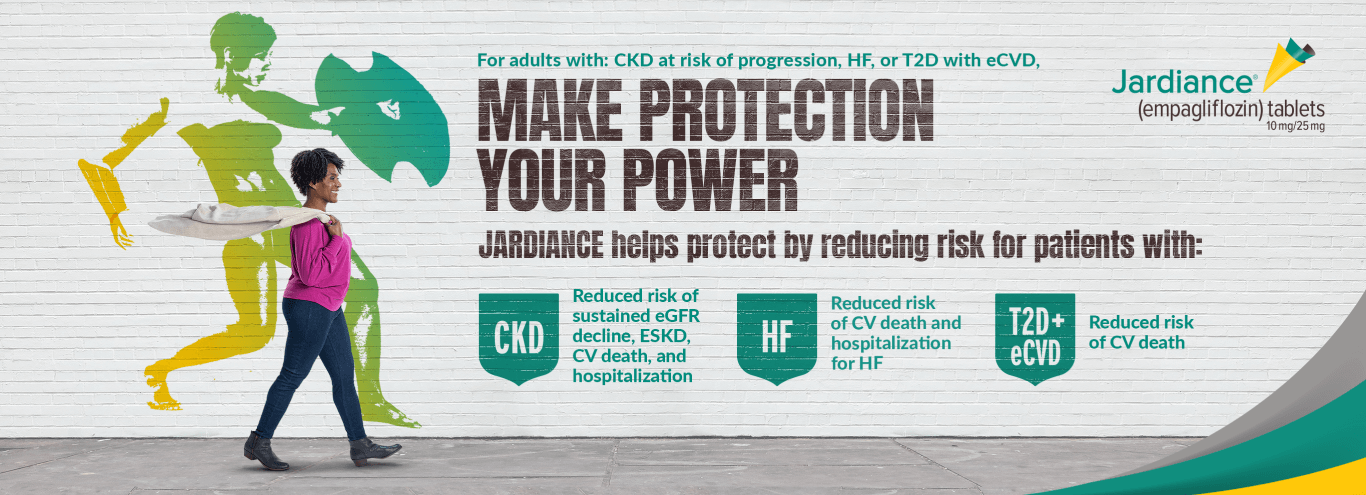
- to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure in adults with heart failure
- to reduce the risk of sustained decline in eGFR, end-stage kidney disease, cardiovascular death, and hospitalization in adults with chronic kidney disease at risk of progression
- to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus and established cardiovascular disease
- as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults and pediatric patients aged 10 years and older with type 2 diabetes mellitus
JARDIANCE is not recommended for use to improve glycemic control in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. It may increase their risk of diabetic ketoacidosis.
JARDIANCE is not recommended for use to improve glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with an eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2. JARDIANCE is likely to be ineffective in this setting based upon its mechanism of action.
JARDIANCE is not recommended for the treatment of chronic kidney disease in patients with polycystic kidney disease or patients requiring or with a recent history of intravenous immunosuppressive therapy or greater than 45 mg of prednisone or equivalent for kidney disease. JARDIANCE is not expected to be effective in these populations.
CONTRAINDICATIONS: Hypersensitivity to empagliflozin or any of the excipients in JARDIANCE, reactions such as angioedema have occurred.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus and Other Ketoacidosis: JARDIANCE increases the risk of life-threatening ketoacidosis in patients with type 1 diabetes and fatal ketoacidosis has occurred with JARDIANCE. Type 2 diabetes and pancreatic disorders are also risk factors for ketoacidosis and fatal events of ketoacidosis have been reported in patients with type 2 diabetes using JARDIANCE. Precipitating conditions for diabetic ketoacidosis or other ketoacidosis include under-insulinization due to insulin dose reduction or missed insulin doses, acute febrile illness, reduced caloric intake, ketogenic diet, surgery, volume depletion, and alcohol abuse. Signs and symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis are consistent with dehydration and severe metabolic acidosis and include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, generalized malaise, and shortness of breath. Assess patients who present with signs and symptoms of metabolic ketoacidosis, regardless of blood glucose levels. If suspected, discontinue JARDIANCE, treat promptly and monitor for resolution before restarting. Consider ketone monitoring in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus as well as in others at risk for ketoacidosis. Withhold JARDIANCE in clinical situations known to predispose to ketoacidosis and resume when clinically stable. Educate all patients on the signs and symptoms of ketoacidosis and instruct patients to discontinue JARDIANCE and seek medical attention immediately if signs and symptoms occur.
Volume Depletion: JARDIANCE can cause intravascular volume depletion which may manifest as symptomatic hypotension or acute transient changes in creatinine. Acute kidney injury requiring hospitalization and dialysis has been reported in patients with type 2 diabetes receiving SGLT2 inhibitors, including JARDIANCE. Before initiating, assess volume status and renal function in patients with impaired renal function (eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2), elderly patients or patients on loop diuretics. In patients with volume depletion, correct this condition before initiating JARDIANCE. After initiating, monitor for signs and symptoms of volume depletion and renal function.
Genitourinary Infections, including Urosepsis, Pyelonephritis, Necrotizing Fasciitis of the Perineum (Fournier’s Gangrene), and Genital Mycotic Infections: JARDIANCE increases urinary glucose excretion and increases the risk of genitourinary infections including urinary tract infections and genital mycotic infections in both males and females. Serious genitourinary infections, including urosepsis, pyelonephritis, and necrotizing fasciitis of the perineum (Fournier’s gangrene, a rare life-threatening infection requiring urgent surgical intervention), have occurred in patients with and without diabetes mellitus receiving SGLT2 inhibitors, including JARDIANCE. Cases have required hospitalization. In patients with Fournier’s gangrene, serious outcomes have included multiple surgeries and death. Patients with a history of chronic or recurrent genitourinary infections are more likely to develop genitourinary infections when using JARDIANCE. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of genitourinary infections and treat promptly. Immediately evaluate patients presenting with pain or tenderness, erythema, or swelling in the genital or perineal area, along with fever or malaise, for necrotizing fasciitis. If suspected, discontinue JARDIANCE and promptly institute appropriate medical and/or surgical intervention.
Hypoglycemia: In adult patients, the use of JARDIANCE in combination with insulin or insulin secretagogues can increase the risk of hypoglycemia. In pediatric patients aged 10 years and older, the risk of hypoglycemia was higher with JARDIANCE regardless of insulin use. The risk of hypoglycemia may be lowered by a reduction in the dose of sulfonylurea (or other concomitantly administered insulin secretagogues) or insulin.
Lower Limb Amputation: Lower limb amputations have been observed in patients with chronic kidney disease taking JARDIANCE. Peripheral artery disease, and diabetic foot infection (including osteomyelitis), were the most common precipitating medical events leading to the need for an amputation. The risk of amputation was highest in patients with a baseline history of diabetic foot, peripheral artery disease (including previous amputation) or diabetes. Counsel patients receiving JARDIANCE about the importance of routine preventative foot care and monitor for signs and symptoms of diabetic foot infection (including osteomyelitis), new pain or tenderness, sores or ulcers involving the lower limbs, and institute appropriate treatment.
Hypersensitivity Reactions: Serious hypersensitivity reactions have occurred with JARDIANCE (angioedema). If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue JARDIANCE, treat promptly, and monitor until signs and symptoms resolve.
MOST COMMON ADVERSE REACTIONS (≥5%): Urinary tract infections and female genital mycotic infections.
DRUG INTERACTIONS:
Diuretics: Coadministration with diuretics may enhance the potential for volume depletion. Monitor for signs and symptoms.
Lithium: Concomitant use with lithium may decrease serum lithium concentrations. Monitor more frequently during JARDIANCE initiation and dosage changes.
USE IN SPECIAL POPULATIONS
Pregnancy: JARDIANCE is not recommended during the second and third trimesters.
Lactation: JARDIANCE is not recommended while breastfeeding.
Geriatric Use: JARDIANCE is expected to have diminished glycemic efficacy in elderly patients with renal impairment. Assess renal function more frequently in elderly patients. The incidence of volume depletion-related adverse reactions and urinary tract infections increased in T2D patients ≥75 years treated with empagliflozin.
CL-JAR-100210 10.24.2025
For more information, please see Prescribing Information, and Medication Guide.